Computed Physical Characteristics of the HD 158259 Planetary System: Semi-Major Axis, Orbital Period, and the Triads Resonance of Successive Planets
New Exoplanet
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55672/hij2022pp46-56Abstract
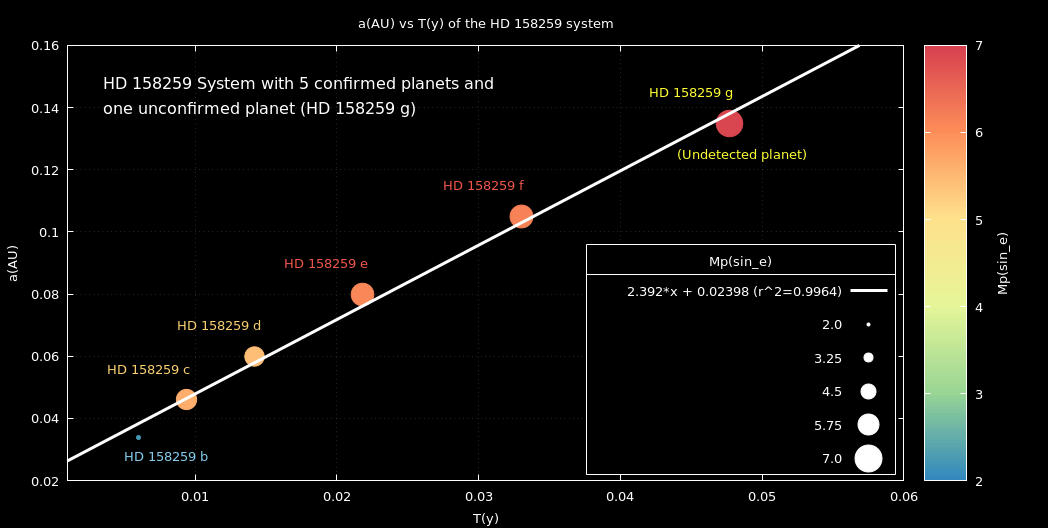
HD 158259 (or HIP 85268) is one of the members of the main sequence in G0 group stars located approximately at 88 light-years away in the constellation Draco, discussed with respect to the solar system. HD 158259 was discovered by the SOPHIE échelle spectrograph using the radial velocity method. This system includes five confirmed planets orbiting HD 158259, together with one unconfirmed planet. The planets orbit in a near 2/3 (or 3:2) orbital resonance. Starting from the innermost pairing, the period ratios are with the period ratios 1.5757, 1.5146, 1.5296, 1.5128, and 1.4482, respectively, starting from the innermost pairing. Here we theoretically investigate the HD 158259 system for the Semi-major axis, planet's mass, star luminosity, inner, center, outer, and ∆(HZ) habitable zone. We account for radial velocity amplitude, planet density, and Laplace’s resonance, theoretically. The existing possibility of the sixth and undetected planet (HD 158259 g) was also investigated. The orbital period and semi-major axis of this planet, computed with 0.047726 years (17.420 days) and 0.135 AU respectively, with ????2 = 0.9964. The radial velocity amplitude of this new and undetected planet was computed to be about 1.625 km/s. The mass of planets in terms of Solar, Jupiter, and Earth have shown direct direct proportional relation with an approximate
increase in their semi-major axis. The lowest mass is closest to the star and the highest mass is farthest from the star. We compare
the habitability zone to that of NASA, Kopparapu et.al, and the original Kopparapu estimate. The application of the relative
mean motion ration (RMMR) for resonance in the triads of successive planets showed that the mode of RMMR is approximately
2/3 (or 3:2) orbital resonance, with the calculated period ratios shown above. we have also calculated the planetary equilibrium temperature (PET) in terms of the size, temperature, Albedo and distance planet to its parent star.
Downloads
References
[1] R. K. Kopparapu et al., "Exoplanet classification and yield estimates for direct imaging missions," vol. 856, no. 2, p. 122, 2018.
[2] U. o. P. R. a. Arecibo. The Planetary Habitability Laboratory (PHL) [Online]. Available: https://phl.upr.edu/home
[3] B. Nikouravan, "Estimating Physical Properties of Confirmed Exoplanets: I. Calculation of essential planetary properties-Possible MR cataloging of exoplanets: Exoplanets New Classification," International Journal of Fundamental Physical Sciences, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 17-29, 2021.
[4] E. E. P. a. NASA. Exoplanet Exploration Program [Online]. Available: https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/
[5] O. E. Catalogue. The planetary system HD 158259 hosts [Online]. Available: http://openexoplanetcatalogue.com/
[6] Exoplanet Exploration Program [Online]. Available: https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu
[7] exofop [Online]. Available: https://exofop.ipac.caltech.edu/tess
[8] B. Nikouravan, "The Prediction of Three Undetected Planets in Kepler-186: Reinvestigated 2021: Astrophysics, Exoplanets," Hyperscience International Journal, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 8-12, 2021.
[9] N. Hara et al., "The SOPHIE search for northern extrasolar planets-XVI. HD 158259: A compact planetary system in a near-3: 2 mean motion resonance chain," vol. 636, p. L6, 2020.
[10] K. G. Stassun et al., "The revised TESS input catalog and candidate target list," vol. 158, no. 4, p. 138, 2019.
[11] A. Brown et al., "Gaia data release 2-summary of the contents and survey properties," vol. 616, p. A1, 2018.
[12] M. C. J. a. p. a. Turnbull, "ExoCat-1: the nearby stellar systems catalog for exoplanet imaging missions," 2015.
[13] T. Exokyoto. List of Exoplanets [Online]. Available: http://www.exoplanetkyoto.org/?lang=en
[14] E. F.-T. TOI. [Online]. Available: https://exofop.ipac.caltech.edu/tess/view_toi.php
[15] J. F. Kasting, D. P. Whitmire, and R. T. J. I. Reynolds, "Habitable zones around main sequence stars," vol. 101, no. 1, pp. 108-128, 1993.
[16] J. J. Rawal, "Resonant structures in the solar system," The moon and the planets, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 407-414, 1981.
[17] S. Dermott, "Bode's law and the resonant structure of the solar system," Nature Physical Science, vol. 244, no. 132, pp. 18-21, 1973.
[18] Understanding Physics. Wiley India Pvt. Limited, 2006.
[19] P. R. Goode et al., "Earthshine observations of the Earth's reflectance," vol. 28, no. 9, pp. 1671-1674, 2001.
[20] m. Petrov, "the influence of the anthropogenic concentration of the atmospheric carbon dioxide on the average global value of earth's albedo."
[21] W. Eric. (2003). Eric weisstein's world of physics. Available: https//:www.wolfram.com/physics
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Hyperscience International Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

 https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0255-2282
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0255-2282 
 https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5172-2204
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5172-2204




 Google Scholar
Google Scholar  Crossref
Crossref  Scopus
Scopus  WorldCat
WorldCat  ORCID
ORCID  Scilit
Scilit  Mendeley
Mendeley  Internet Archive
Internet Archive